Ch 9 Bill of Rights & Other Amendments
"A right is something the government can't do to you." (Senator Mike Lee)
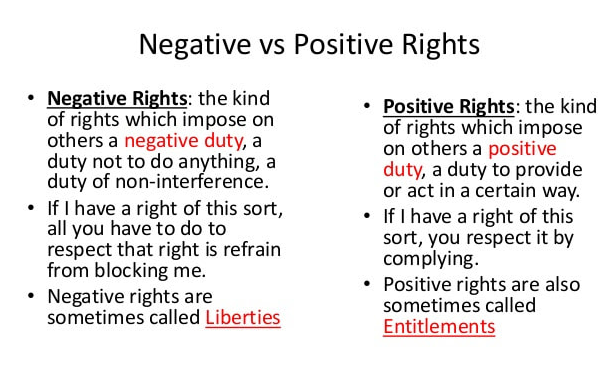
Negative Rights and Positive Rights
Redefinition of Rights
FDR's Second Bill of Rights
FDR's Second Bill of Rights
Near the end of World War II, FDR proposed a "Second Bill of Rights" that would fundamentally transform the nature of rights. He believed that people should have rights to have certain things provided to them by the State! (A right to get something from the government is a "positive right." It means that others have a duty to provide something to you.) This signaled a 180 turn from the Constitutional view of rights as articulated in the Bill of Rights. According the founding principles, people have natural, inherent rights to life, liberty, and property, and the Bill of Rights was designed to protect people from the government encroaching upon these pre-existing, inherent rights. (A right to be protected from encroachment is a "negative right." It means that others have a duty to refrain from infringing on your life, liberty, or property.) FDR was proposing a new definition of rights that placed a duty on some to provide something to others. Thus, FDR's approach involved a perspective toward rights that would deny some people their natural rights while providing nice things to others in exchange for votes.
A right to get something from the government is a "positive right." It means that others have a duty to provide something to you. The Social Justice movement, Progressivism, Leftism, Socialism, and Marxism are based on this view of rights.
A right to be protected from encroachment is a "negative right." It means that others have a duty to refrain from infringing on your life, liberty, or property. America's Constitution was based on this view of rights.
A right to be protected from encroachment is a "negative right." It means that others have a duty to refrain from infringing on your life, liberty, or property. America's Constitution was based on this view of rights.
There are two ways to understand what a right actually is. Negative rights provide citizens “freedom from” governmental intrusion. They prohibit government from acting. Positive rights, on the other hand, require government to act in order to provide “freedom to” do or enjoy certain things. Can these two types of rights coexist within the same regime?
For more information on John Locke and Natural Rights
Bill of Rights!
|
|
|